PERIODONTICS AND DENTAL DISEASE CARE
Periodontics is the branch of dentistry focused on treating periodontal disease. If not adequately treated, this condition is one of the main causes of tooth loss and can be associated with other chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
How does periodontitis develop?
Essentially, it occurs when there is an accumulation of bacterial plaque that allows harmful bacterial populations to prevail in the gingival sulcus. These bacteria can then cause a true infection, which, in turn, stimulates our immune system.
This process results in the establishment of an inflammatory process, usually chronic, for defence.
What are the consequences of periodontal diseas?
The inflammatory process generally affects the supporting apparatus of the tooth. It may involve only the gums, in which case gingivitis will develop; if the underlying structures, bone, and periodontal ligament, are also affected, periodontitis will develop.
How can I tell if I have this disease?
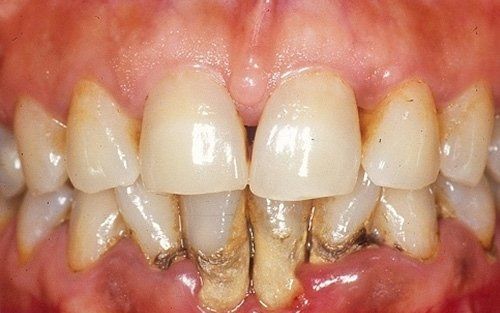
Periodontal disease is often silent, meaning it does not cause specific symptoms, especially pain, until an advanced stage of the disease. However, there are clear signs that, with careful examination, allow for a precise diagnosis in a timely manner for disease treatment:- Redness, swelling, and tenderness at the gum level
- Presence of bleeding when using a toothbrush or dental floss
- Receding gum line: "my teeth appear longer"
- Increased tooth mobility
- Increased interdental spaces or changes in tooth position
- Presence of "pus" in the gingival sulcus
- Persistent bad breath
Gengivitis
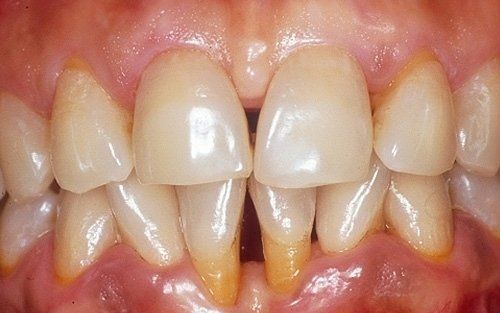
This is the mildest form of periodontal disease. The gums appear red, swollen, and bleed easily. Symptoms are mild and do not go beyond modest tenderness. Gingivitis is commonly caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Factors that may contribute to gingivitis include diabetes, smoking, systemic diseases, stress, hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, substance abuse, HIV infection, and the use of certain medications. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and adequate home oral hygiene practices.
How is gengivitis treated?
Gingivitis is a reversible phenomenon easily treatable with non-surgical professional treatment and adequate home oral hygiene practices.
Periodontitis
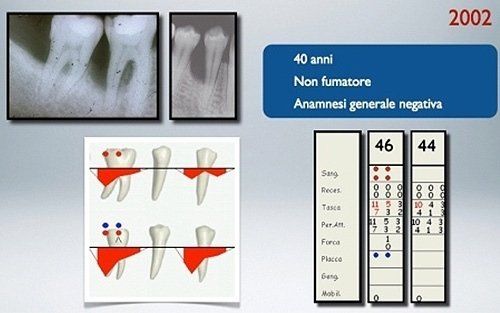
It is the most severe form of disease treated in periodontics: it is characterised not only by the typical signs of gingivitis but also by the destruction, in part or completely, of the supporting apparatus of the teeth.
What is the process that leads to the appearance of this form of periodontal disease?
Can periodontitis be cured?
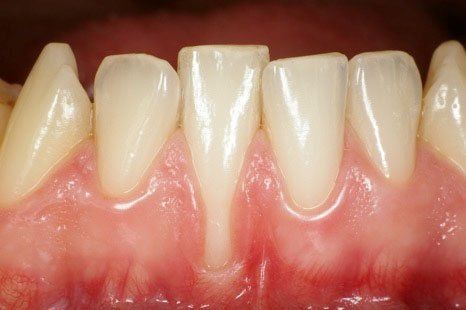
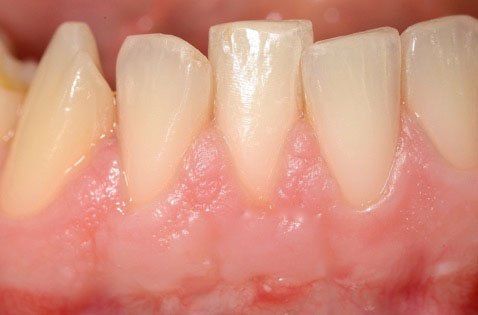
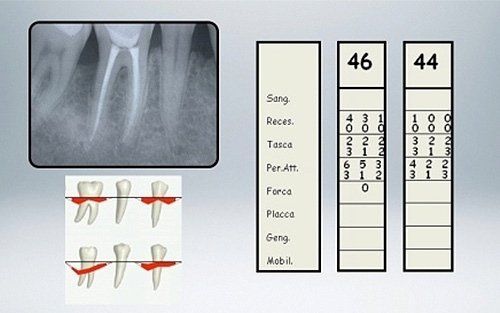
Certainly! However, it is necessary to eliminate what caused the periodontal disease, bacterial infection, and then undergo periodontal therapies capable of eliminating the defects affecting the tooth's supporting tissues (bone and periodontal ligament) that periodontitis typically causes.
What are, then, the possible therapies?
Our periodontal treatments for the treatment of periodontitis are based on the conviction that periodontal health should be achieved through the least invasive and most cost-effective treatment. This is often achieved through non-surgical periodontal treatment. However, it is necessary to keep in mind the limits of non-surgical treatment: only when it does not achieve periodontal health, then surgery may be indicated to restore healthy periodontal structures.
- Scaling and root planing: this is a thorough cleaning of the root surfaces to remove plaque and tartar from deep periodontal pockets and to smooth the root surface to eliminate bacterial toxins.
- Flap surgery: during these procedures, soft tissues (gums) are incised and subsequently lifted to allow for the complete removal of bacterial deposits present on the root walls; after decontamination, the tissues are repositioned and held in place by applying sutures. Sometimes, it is necessary to regularise the altered bone profile to eliminate all the roughness where new bacterial deposits can accumulate.
- Regenerative therapies: these procedures are based on the complete elimination of bacteria colonising the bone defect to be treated, and the subsequent application of membranes with the possible association with special materials that stimulate the production of new tissues, especially bone tissues.