FIXED AND REMOVABLE PROSTHETICS
Prosthetic dentistry is the branch of dentistry that deals with
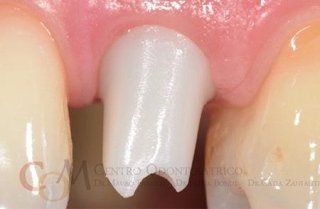
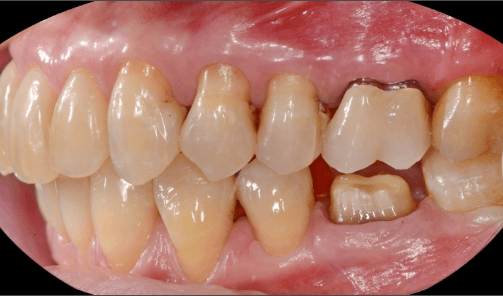
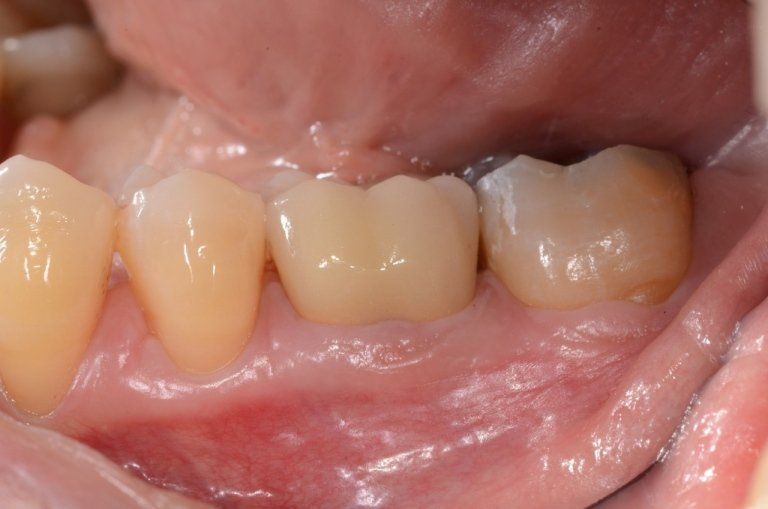
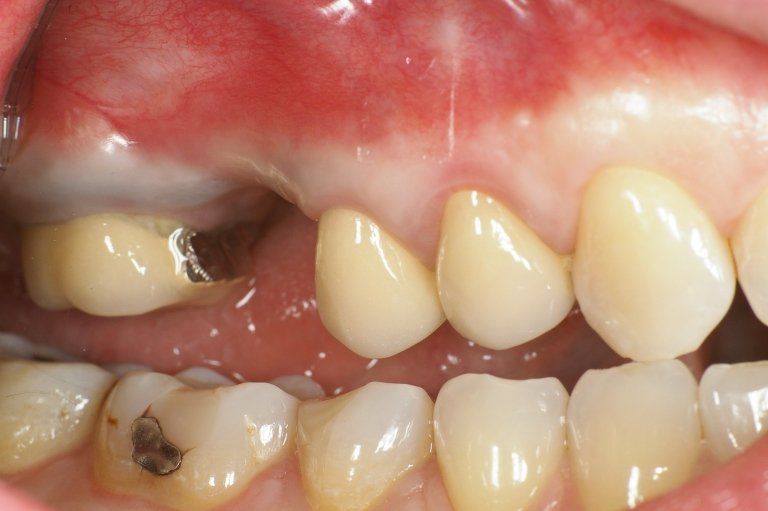
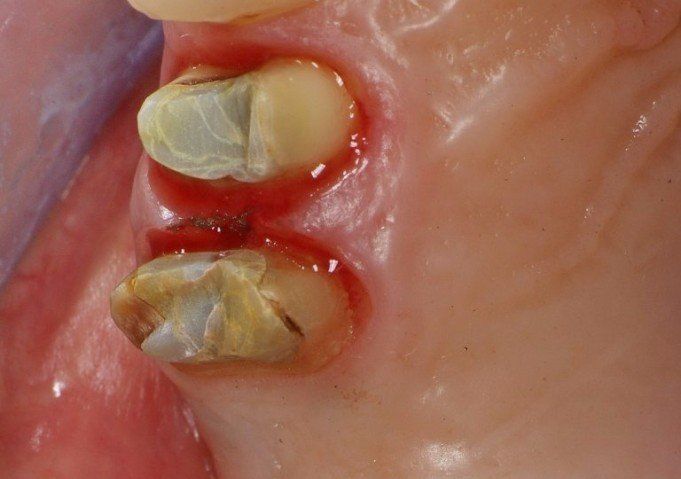
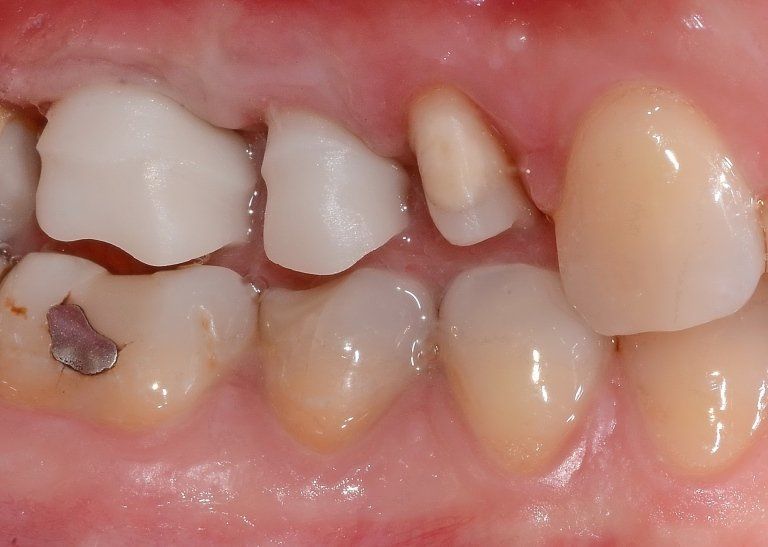
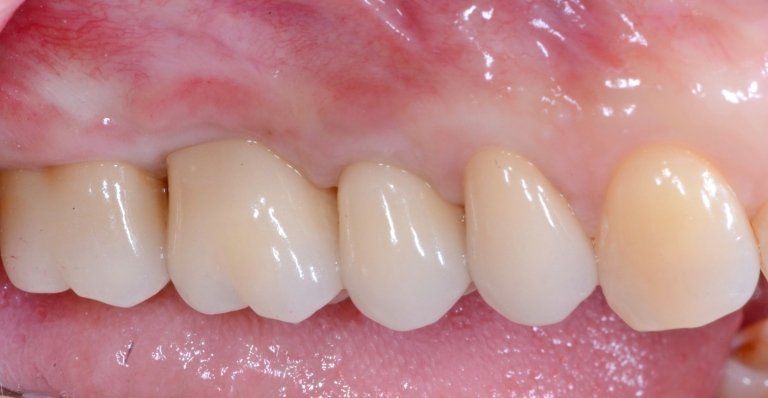
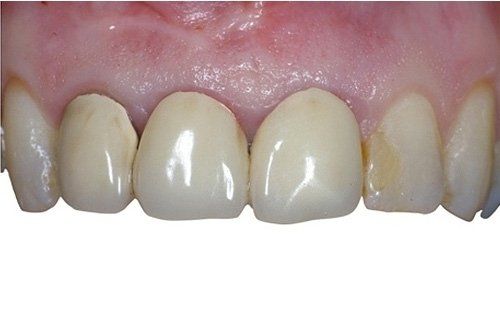
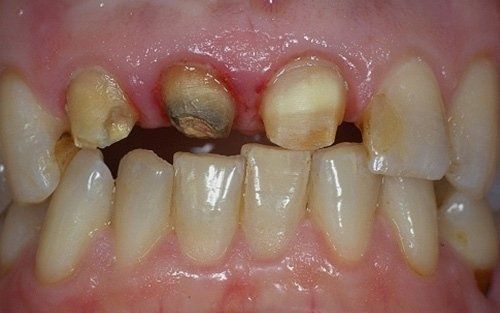
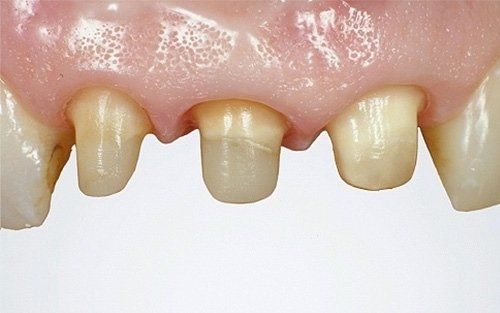
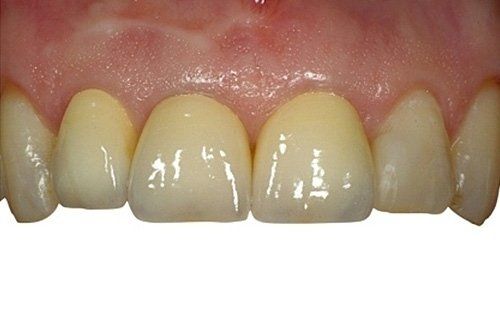
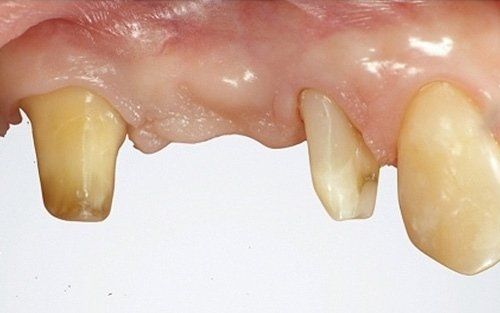
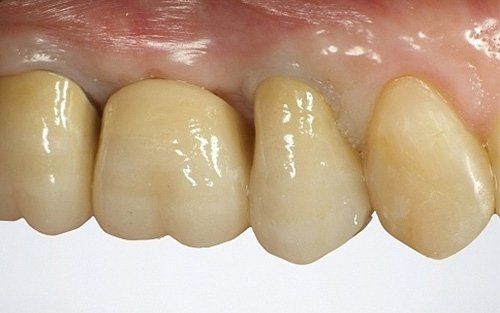
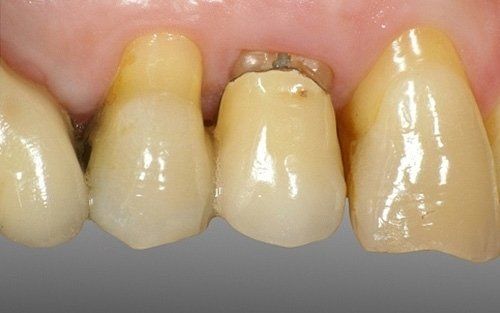
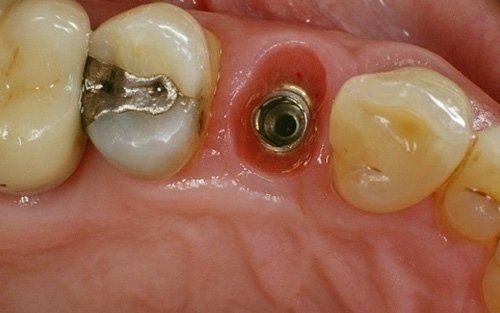
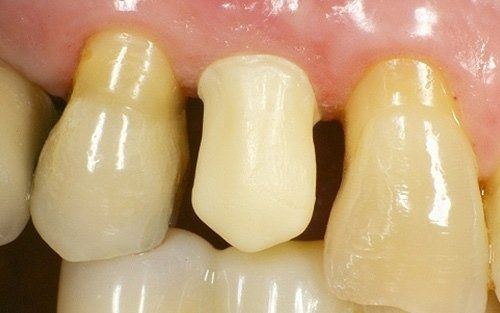
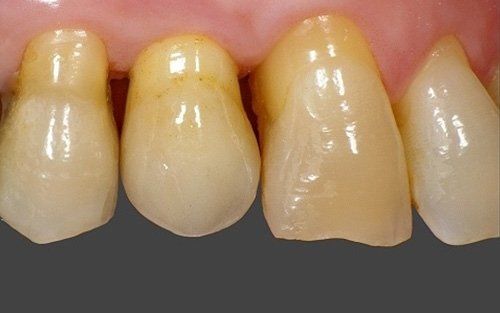
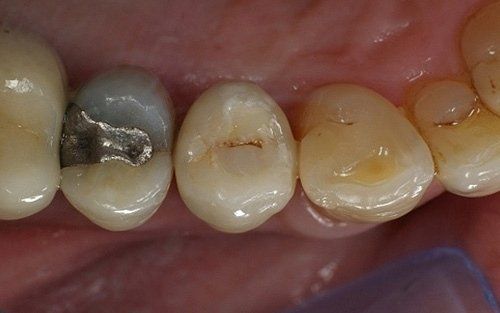
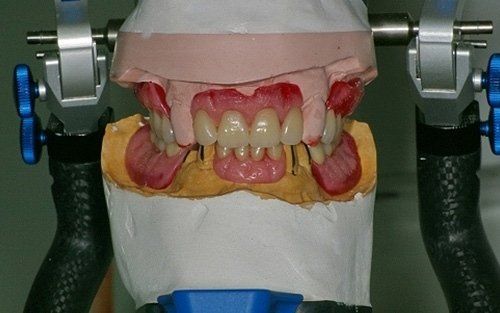
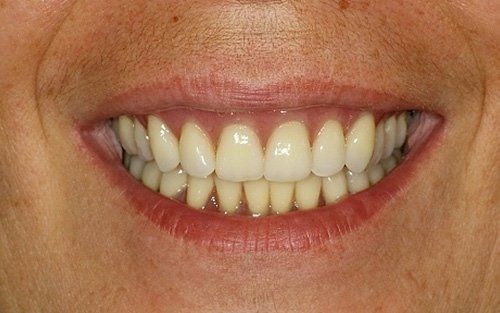
restoring and maintaining chewing function through the restoration of natural teeth and/or the replacement of missing teeth and adjacent oral tissues using artificial devices. Fixed prosthetics involves the restoration and/or replacement of teeth using structures that cannot be removed from the mouth. With this type of prosthesis, in the form of single crowns or bridges, it is possible to
reconstruct and/or improve the shape, functionality, and aesthetics of severely compromised teeth in all those cases where it is not possible to apply simpler forms of restoration (see dedicated section on direct and indirect restorative dentistry).
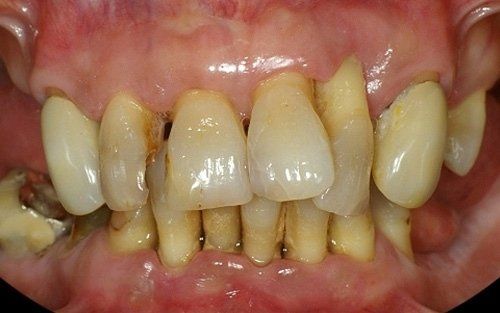
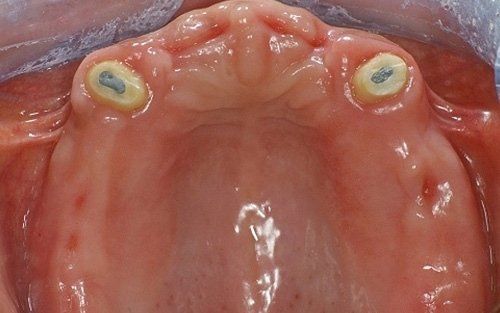
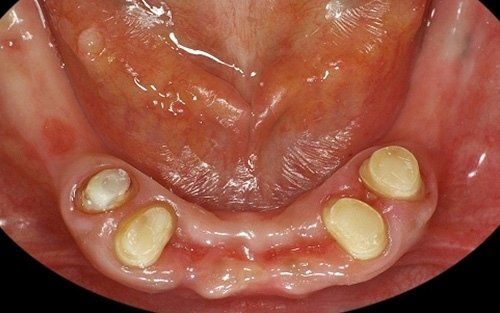
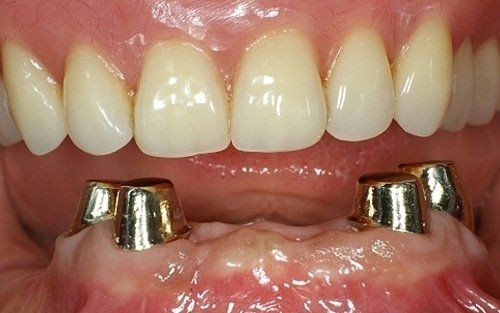
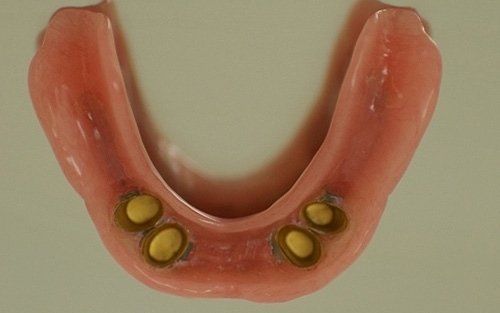
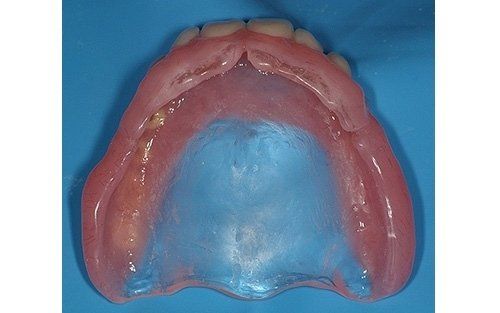
Removable prosthetics allow for the replacement of teeth and adjacent structures in patients who are totally or partially edentulous using artificial structures that can be removed from the mouth. In the case of partial prostheses, the choice (in contrast to a fixed solution) depends on the number, position, and conditions of the supporting structures of the existing abutment teeth.
Total prosthetics are necessary to compensate for the complete loss of the dentition in one or both arches; it is essential that their fabrication accurately respects the remaining oral structures in order to ensure their long-term maintenance.